| MetriVis | Overview | Download | User Manual | Development |
| Reference | Overview | Design Documentation | Reference Backend | Reference Frontend |
#include <Thread.h>

Public Member Functions | |
| Thread () | |
| Initializes the Thread. | |
| virtual | ~Thread () |
| Initializes the Thread. | |
| virtual int | Init () |
| Initializes the Thread. Default implementation sets internal state. | |
| int | Start () |
| Starts the Thread. | |
| int | Stop () |
| Stops the Thread. | |
| int | StopBlocking () |
| Asks to stop the thread and blocks until thread finished. | |
| virtual int | Uninit () |
| Initializes the Thread. Default implementation sets internal state. | |
| int | RunBlocking () |
| Doesn't create a system thread but executes the main loop manually. | |
| void | Wait () |
| Stops the current thread until the other thread finished working. | |
| boost::thread & | thread () const |
| Interface function to internal thread object. | |
| bool | IsRunning () const |
| Interface function to internal Thread state. | |
| void | set_name (const std::string &name) |
| Interface function to thread name. | |
| const std::string & | name () const |
| Interface function to thread name. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | Run ()=0 |
| Threading code. Will be run after thread start. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| volatile bool | running_ |
| True if the thread is running. | |
Private Types | |
| enum | State { UNUSED = 0, INITIALIZED, RUNNING } |
| The internal state representation. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | InternalRun () |
| Wrapps itself around abstract Thread::Run for state setting. | |
Private Attributes | |
| State | internal_state_ |
| Representation of internal state. | |
| boost::thread * | thread_ |
| Internal thread reference. | |
| boost::mutex | run_mutex_ |
| Mutex locks running/stopping changes. | |
| std::string | name_ |
| The name of the thread. | |
Each thread object represents a thread in user-space. This class offers a similar interface as Java-Threads. Threads hold internal state informations that help the class to manage the thread-state , it may be: [UNUSED, INITIALIZED, RUNNING].
Every thread needs to be used in the following order:
Thread t; t.Init() t.Start(); t.Stop(); t.Uninit();
A thread use in your code like this:
Some remarks on the implementation: Don't forget to set the Thread state if you are overloading Thread::Init or Thread::Uninit:void MyThread::Init() { //This will call the underlaying Thread::Init() function. Thread::Init(); // Do your own stuff here... }
enum metrivis::Thread::State [private] |
The internal state representation.
Represents the state a thread may be in. The thread is not running unless the
Thread::internal_state_ == RUNNING
| metrivis::Thread::Thread | ( | ) |
| metrivis::Thread::~Thread | ( | ) | [virtual] |
| int metrivis::Thread::Init | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initializes the Thread. Default implementation sets internal state.
Initializes the Thread.
Initializes the Thread class. The default implementation of this function just sets internal state informations to the initialized state. Call this function always or set the Thread::internal_state_ manually to INITIALIZED.
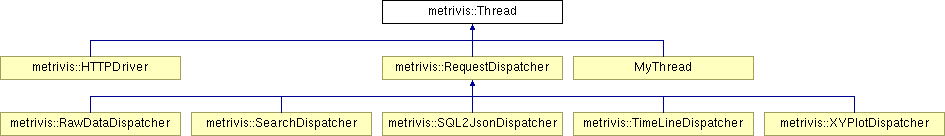
Reimplemented in metrivis::HTTPDriver, MyThread, metrivis::RawDataDispatcher, metrivis::SearchDispatcher, metrivis::SQL2JsonDispatcher, metrivis::TimeLineDispatcher, and metrivis::XYPlotDispatcher.
| int metrivis::Thread::Start | ( | ) |
Starts the Thread.
This function starts the thread. It will call Thread::Run, where the thread code is executed.
| int metrivis::Thread::Stop | ( | ) |
Stops the Thread.
This function stops the thread. It will set the internal state information to
INITIALIZED
| int metrivis::Thread::StopBlocking | ( | ) |
Asks to stop the thread and blocks until thread finished.
Stops the Thread, blocks until it finishes.
The same as boost::thread::join(). The current thread of execution blocks until the initial function of the thread of execution represented by *this finishes and all resources are reclaimed.
| int metrivis::Thread::Uninit | ( | ) | [virtual] |
Initializes the Thread. Default implementation sets internal state.
Uninitializes the Thread.
Uninitializes the Thread class. The default implementation of this function just sets internal state informations to the initialized state. Call this function always or set the Thread::internal_state_ manually to
UNUSED
Reimplemented in metrivis::HTTPDriver, MyThread, metrivis::RawDataDispatcher, metrivis::SearchDispatcher, metrivis::SQL2JsonDispatcher, metrivis::TimeLineDispatcher, and metrivis::XYPlotDispatcher.
| int metrivis::Thread::RunBlocking | ( | ) |
Doesn't create a system thread but executes the main loop manually.
Runs the thread code without spawning a thread.
Just starts the main loop manually. Blocks until Thread::Stop is called.
| void metrivis::Thread::Wait | ( | ) |
Stops the current thread until the other thread finished working.
Stops the Thread, blocks until it finishes.
The funtion won't return until the thread finished it's work.
| boost::thread& metrivis::Thread::thread | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Interface function to internal thread object.
| bool metrivis::Thread::IsRunning | ( | ) | const [inline] |
| void metrivis::Thread::set_name | ( | const std::string & | name | ) | [inline] |
Interface function to thread name.
| name,: | String representing the thread name. |
| const std::string& metrivis::Thread::name | ( | ) | const [inline] |
Interface function to thread name.
| virtual void metrivis::Thread::Run | ( | ) | [protected, pure virtual] |
Threading code. Will be run after thread start.
Is executed threaded after call to Thread::Start. The function should contain non blocking functions so that the thread may terminate after Thread::Stop is called. A typical main loop may look like this:
while( running_) { //do some stuff }
Implemented in metrivis::HTTPDriver, MyThread, metrivis::RawDataDispatcher, metrivis::RequestDispatcher, metrivis::SearchDispatcher, metrivis::SQL2JsonDispatcher, metrivis::TimeLineDispatcher, and metrivis::XYPlotDispatcher.
| void metrivis::Thread::InternalRun | ( | ) | [private] |
Wrapps itself around abstract Thread::Run for state setting.
Internal run function for the Thread.
This function will call the virtual and abstract Thread::Run function.
 1.5.3
1.5.3